Mapapi
System Architecture
This document provides an overview of the system architecture for the Mapapi project. It outlines the main components, data flow, and interactions within the system.
Overview
Mapapi is designed to manage and visualize environment-related incidents. The architecture is built to support scalability, reliability, and efficient data processing.
Components
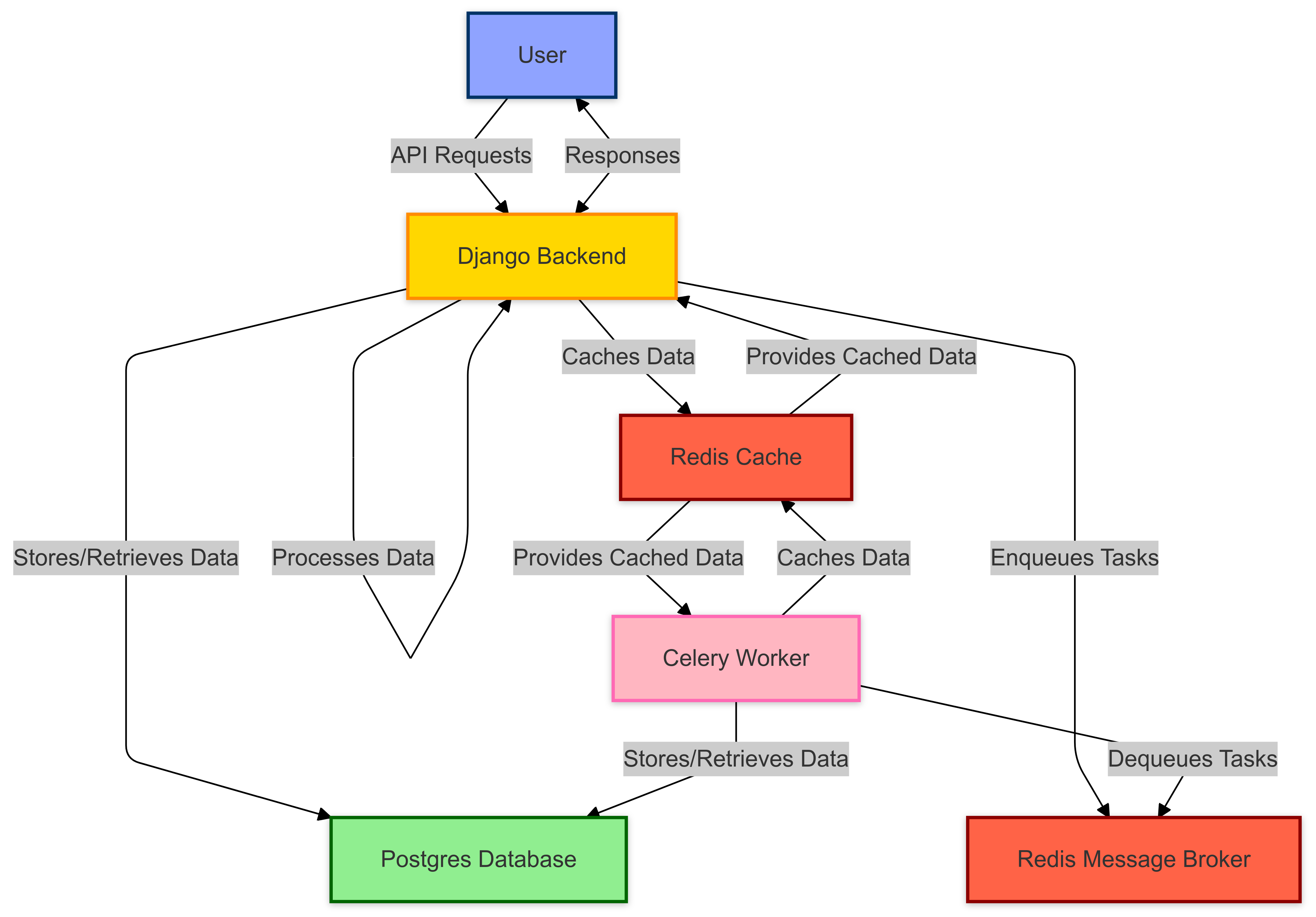
- Django Backend: Serves as the core of the application, handling API requests, business logic, and data management.
- Postgres Database: Stores user data, incident reports, and other persistent information.
- Celery: Manages asynchronous tasks, such as sending notifications and processing data in the background.
- Redis: Acts as a message broker for Celery and provides caching capabilities to improve performance.
Data Flow
- API Requests: Users interact with the system through RESTful API endpoints provided by the Django backend.
- Data Processing: Incoming data is validated and processed by the backend, with tasks delegated to Celery for asynchronous handling.
- Database Operations: Data is stored and retrieved from the Postgres database, ensuring consistency and reliability.
- Caching and Messaging: Redis is used to cache frequently accessed data and facilitate communication between components.
Diagrams
Conclusion
The Mapapi architecture is designed to efficiently handle a wide range of operations related to environment-related incidents. By leveraging Django, Postgres, Celery, and Redis, the system provides a robust and scalable solution.
For more detailed information, refer to the individual component documentation and source code.